
-
By admin
-
February 20, 2026
- 0 Comment
What is an Ethernet Cable? – Types, Categories, Shielding, and More
Ethernet cables let users connect their devices to local (LAN) and wide area networks. The most common devices that can be connected using an Ethernet cable are smartphones, computers, laptops, and security cameras. These cables are known for their blazing-fast, more stable internet connection than WiFi.
They have been crucial components of digital setups or wired networks. Their main purpose is to let users connect to the Internet, transfer information from one point to another, and communicate with each other in real-time. They are everywhere! Even right now, while you read this article online, Ethernet cables are playing their vital role behind the scenes to transmit data quickly, reliably, and without any interruptions.
This article explains Ethernet cables in detail. Let us understand how the everyday network you use heavily relies on Ethernet cables. We will focus on the technical differences between different types of Ethernet cables.
What is an Ethernet Cable?

An Ethernet cable connects a device, like a computer, to the LAN. It is a physical wire that contains twisted copper conductors within a protective sheath. All Ethernet-connected devices can communicate with each other at high speed. These cables are ideal for tasks such as streaming, gaming, and large file transfers.
In 1973, while working at Xerox PARC, Robert Metcalfe co-founded the first functional Ethernet system using thick coaxial cables. It used to connect devices such as printers and computers in the lab. Due to its high-speed, more stable data transmission capabilities, the Ethernet cables quickly gained immense popularity.
Today’s Ethernet cables support higher bit rates, more devices, and faster, more stable data transmission than before. At Wider Cable, we manufacture Ethernet cables that support frequencies up to 2000 MHz and data transmission speeds of up to 40 Gbps. All cables feature S/FTP dual shielding for superior EMI protection.
Ethernet Cable Categories (Types of Ethernet Cables)
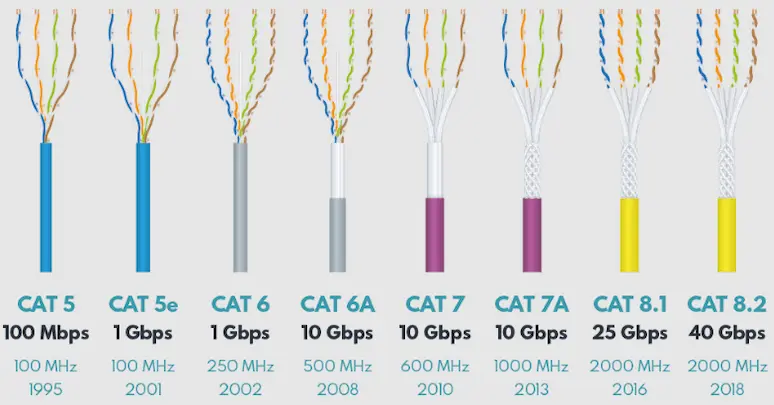

Ethernet cables are classified into different categories based on their performance characteristics, such as bandwidth, speed, shielding, connectors, and more. This classification is known as the Ethernet cable categories (CAT).
So, let us discuss what CAT is in Ethernet cables?
Most of the time, users get the Ethernet cable for free with the device that uses Ethernet connectivity. However, understanding the difference between various types of Ethernet cable helps them choose the perfect cable for their scenario.
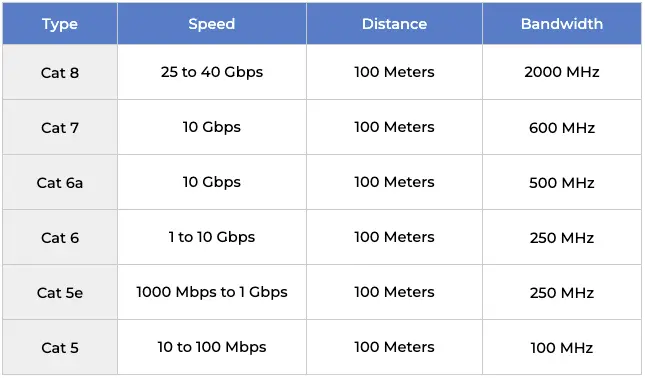
1. Cat 8
Cat 8 is the most advanced Ethernet category. The Cat 8 Ethernet Cables are mainly used in large data centers and other high-speed industrial network setups. All Cat 8 cables are fully shielded to prevent interference and enable higher data rates.
- 2000 MHz Bandwidth
- 40 Gbps speed up to 30 meters
- Overall and Individual Pair Shielding
- Ideal for high-performance computing and server rooms
The Cat 8 Ethernet cables are pretty rigid and can be challenging to install in tight spaces. They are considered to be over-engineered for home applications.
2. Cat 7
These are the affordable alternatives to Cat 8 cables. They are known for providing excellent signal integrity and a stable internet connection. The Cat 7 cables are the best suited for medium-scale offices, including multiple devices, where the chances of electromagnetic interference are high.
- 600 MHz Bandwidth
- 10 Gbps Speed up to 100 meters
- Overall and Individual Pair Shielding
- Ideal for corporate buildings, professional server rooms, and multi-device offices
There is an augmented or advanced version of Cat 7 Ethernet cables. It is known as Cat 7a, where the “a” stands for Augmented. Such cables are capable of offering 40 Gigabit speeds up to 50 meters.
3. Cat 6
Cat 6 cables are mainly used for home and office applications. They are ideal for scenarios that demand better internet speed with minimal interference. These cables are mostly unshielded.
- 250 MHz Bandwidth
- 1 Gbps Speed up to 100 meters
- Unshielded or Overall Shielding
- Ideal for gaming, HD streaming, and average office network requirements
At most, the Cat 6 Ethernet cables include an overall foil shield (F/UTP) for reducing interference. The aluminium foil shield is not as effective as braided shielding in ensuring long-term EMI protection.
4. Cat 6a
The Cat 6a cables are the augmented version of Cat 6 cables. They are best suited for high-demand home or modern business networks. These cables support 10 Gbps speeds at frequencies of 500 MHz.
- 500 MHz Bandwidth
- 10 Gbps speed up to 100 meters
- Overall and Individual Pair Shielding
- Ideal for advanced home and office networks
Please note that a few Cat 6a cables feature braided overall shielding as per the requirements.
5. Cat 5
The Cat 5 cables are outdated nowadays. They were the standard for Ethernet connections for more than 2 decades. These cables are rarely manufactured by anyone today due to their limited speed and bandwidth. The Cat 5 cables were mainly used for distributing data, video and telephone signals at distances up to 100 meters.
- 100 MHz Bandwidth
- 100 Mbps Speed
- Mostly Unshielded
- Ideal for basic internet requirements and networking tasks
The most common alternatives to this cable are Cat 5e and Cat 6 cables. With them, at a fraction of extra cost, you get enhanced performance for your home networks.
6. Cat 5e
The “e” in Cat 5e stands for Enhanced. These cables are an advanced or improved version of Cat 5 cable. They can support up to 1 Gbps speed and have the ability to resist crosstalk or interference. Their advanced specs are achieved by increasing the number of twists.
- 100 MHz Bandwidth
- 1 Gbps Speed
- Unshielded or Only Overall Shielding
- Ideal for most home and small office networks
Due to its reliable performance and affordability, the Cat 5e cable is still a popular choice over Cat 6 and Cat 6a cables.
Types of Ethernet Cables - Comparison Table
Here is a quick comparison table explaining the differences between different cable categories:
Ethernet Cable Shielding Types
Electromagnetic signals from adjacent power lines, cables, or even the machinery can reduce the performance of an Ethernet cable. This phenomenon is known as EMI (electromagnetic interference).
The manufacturers use shielding to prevent the potential signal interruptions from EMI and crosstalk. The shielding is a layer of aluminium foil or braided copper that surrounds the cable. In the case of Ethernet cables, the shield is wrapped around the entire cable or each twisted pair individually.
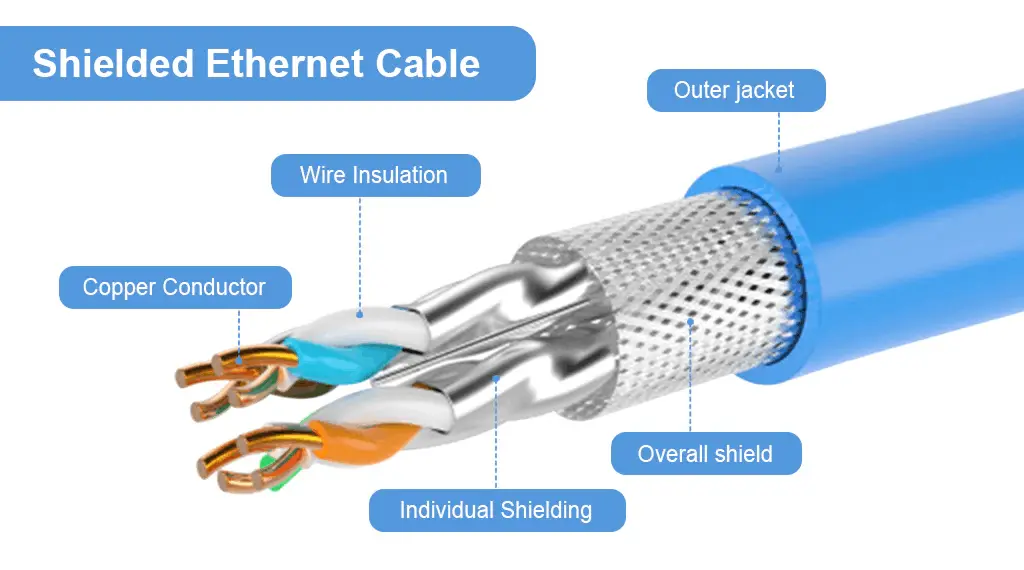
A code is used to describe the type of shielding used in the given cable. You can see that code printed on the wire itself. The general terms used in that code or notation are as follows:
- U stands for Unshielded
- F stands for Foil Shield
- S stands for Braided Screen
- TP altogether stands for Twisted Pair
For example, suppose that if the overall wire is foil shielded and individual pairs are unshielded, then the F/UTP code will be printed on the Ethernet cable.
Below, we have discussed the most common shielding types:
1. U/UTP (Unshielded Overall Cable and Unshielded Twisted Pairs)
It represents an entirely unshielded Ethernet cable. The UTP Ethernet cable is ideal for environments with minimal or negligible electromagnetic interference (EMI).
The UTP is a short abbreviation for U/UTP. A plastic spline in the centre os these UTP Ethernet cables prevents the crosstalk from the internal twisted pairs. Due to the absence of aluminium foil and braided screen, UTP Ethernet cables are thinner and more flexible than their shielded counterparts. As such, these cables are easier to install.
2. F/UTP (Foil Shielded Overall Cable and Unshielded Twisted Pairs)
In this type of shielding, a thin layer of aluminium foil is wrapped around the entire cable, beneath the jacket. Whereas the individual twisted pairs are unshielded. The F/UTP Ethernet cables have a simple design and excellent performance.
The F/UTP cables are often referred to as FTP cables. Such shielding uses a drain wire to redirect unwanted noise to ground.
3. S/UTP (Braid Shielded Overall Cable and Unshielded Twisted Pairs)
In contrast to the F/UTP cables discussed above, the S/UTP cables include a braided copper shield wrapped around the entire cable, beneath the jacket. The braided shields offer enhanced mechanical strength and protection from radio frequency interference (RFI).
The S/UTP Ethernet cable shielding is commonly known as the STP. The STP cables are ideal for environments with high electromagnetic interference.
5. U/FTP (Unshielded Overall Cable and Foil Shielded Twisted Pair)
This is one of the most popular Ethernet cable shieldings, where each individual twisted pair is wrapped with aluminium foil, and the entire cable is kept unshielded. It is the more economical and practical choice over UTP and F/UTP cables.
Their key benefit is the lack of a plastic spine used in cables with other shielding types to prevent crosstalk. Due to the absence of a plastic spine, these cables are more flexible and easier to install.
4. S/FTP (Braid Shielded Overall Cable and Foil Shielded Twisted Pairs)
The S/FTP shielding offers superior EMI protection. It includes a copper braid jacket around the entire cable and aluminium foil wrapped around the individual twisted pair. Due to the presence of dual shielding, Ethernet cables utilising these shields are thicker and less flexible. The dual shielding maintains signal quality over longer distances and at higher speeds.

This type of Ethernet cable shielding is ideal for industrial networks and outdoor setups. The S/FTP shielding is commonly known as the SSTP or SFTP shielding. Companies like Wider Cable use SSTP shielding across all category cables for the highest level of protection against EMI and RFI. Such strong shielding provides the best possible security against data eavesdropping. Despite the added complexity and material requirements of S/FTP cable manufacturing, Wider Cable delivers premium-performance cables at unmatched pricing.
6. F/FTP (Foil Shielded Overall Cable and Foil Shielded Twisted Pairs)
Both individual twisted pairs and the overall cable are shielded with a thin layer of aluminium foil in this type of shielding. The dual shield offers excellent protection against electromagnetic interference. The F/FTP cables are also known as the fully shielded Ethernet cables, similar to the S/FTP cables.
The F/FTP cables are more cost-effective than S/FTP or SSTP cables. However, they are less durable and cannot withstand harsh outdoor environments. That’s why S/FTP is used in outdoor Ethernet cables, and F/FTP is used in indoor Ethernet cables.
7. SF/UTP (Braid and Foil Shielded Overall Cable and Unshielded Twisted Pairs)
In this type of shielding, both the aluminium foil and copper braid are wrapped around the entire cable and the individual twisted pairs are kept unshielded. The SF/UTP shielding is ideal for a noisy environment. It can resist a wider range of electromagnetic interference frequencies.
Consider this shielding as an advanced upgrade to S/UTP or F/UTP shielding.
8. SF/FTP (Braid and Foil Shielded Overall Cable and Foil Shielded Twisted Pairs)
The SF/FTP cable uses triple shielding for maximum performance and protection. They have a pair of copper braid and aluminium foil wrapped around the entire cable, beneath the jacket. Moreover, all individual pairs are wrapped in separate aluminium foils for the best-in-class performance. As such, this type of shielding offers protection against all types of interruptions, including internal and alien (external) crosstalk, EMI, ESD, RFI, and more.
However, it is worth noting that this type of construction makes the SF/FTP cables bulky and less flexible. That’s why they are only used across industrial applications that require the top-notch network quality and protection against threats.
If you are having trouble choosing the best suitable shielding for your application, contact our team of experts at Wider Cable. Our team has 20+ years of experience manufacturing and supplying industrial-grade Ethernet cables for data centres, enterprise-grade offices, and OEMs.
Most Common Uses of Ethernet Cable
Ethernet used to be another name for the Internet back in the 1990s. Without any doubt, the Ethernet technology holds so much importance in today’s digital era. However, as the WiFi technology grew in popularity, Ethernet has become less well-known. Ethernet’s role shifted from end-user visibility to core network infrastructure.
Below are the common uses of Ethernet cables:
- LAN Connectivity: Local Area Networks (LANs) heavily depend on Ethernet cables. They are the fundamental building blocks of a LAN system. Their unmatched performance makes them the best choice for creating a high-performance LAN. It allows users to connect computers, printers, servers, and switches together within their homes, offices, and commercial buildings.
- WiFi Connectivity: Ethernet cables are used to connect a WiFi router or modem to the telephone line or internet entry port. It ensures stable, high-speed Internet for even the heavy users.
- Data Centres and Server Rooms: Interconnecting servers, storage systems, and networking equipment for low-latency, high-bandwidth communication.
- Business Networks: Ensures secure, scalable wired communication across various devices connected to enterprise and corporate networks.
- Heavy-Duty OT Networking: Ethernet cables are the first choice for creating secure communication between machines, controllers, sensors, and monitoring systems in heavy-duty industrial and manufacturing environments.
- Streaming and Gaming: Enables high-performance gaming and reliable streaming through low-latency, stable connections.
- Outdoor Connectivity: Connecting outdoor equipment, such as Starlink satellite dishes and network terminals. It is also used to connect buildings, access points, and outdoor equipment across campuses, warehouses, and industrial sites.
- IP Surveillance Systems: The PoE Ethernet cables are used for both powering and transmitting data to IP cameras, NVRs, and security monitoring systems.
- Telecommunications & ISP Infrastructure: The PoE cables are also crucial for devices such as wireless access points, VoIP phones, and smart lighting.
Top 6 Limitations of Ethernet Connectivity
The Ethernet technology has evolved drastically since its inception. However, there are several well-known technical limitations that must be considered.
- Cable Length: Ethernet cables are ideal for up to 100 meters of transmission. Beyond this distance, the signal weakens due to attenuation. It results in data errors.
- Cable Management: In the case of large and complex buildings, offices, campuses, outdoor environments, and more, it becomes cumbersome to manage multiple Ethernet cables.
- Electrical Interference: Electrical signals from neighbouring devices or even the cables can reduce the overall efficiency and transmission rate of Ethernet cables. The issue becomes more serious in electrically noisy environments.
- Outdoor Environment: The users can not use standard Ethernet cables outdoors. They need specialized outdoor Ethernet cables that are equipped with a waterproof, UV-resistant jacket capable of withstanding harsh environments.
- Mobility: The devices connected to Ethernet are tied to a particular space or area. They tether devices to a fixed location, and not as flexible as WiFi connectivity.
- Installation Cost: The cost increases significantly as you choose the higher category cable. For example, the Cat 8 cables are very expensive compared to Cat 6 cables. Additionally, they require physical routing, conduits, and trenching, which again requires both extra time and more money.
- Vulnerability to Physical Damage: Ethernet cables are susceptible to bending, crushing, moisture, UV exposure, and more environmental threats.
Wider Cable: Leading Manufacturer of Industry-Grade Ethernet Cables
Wider Cable has 20+ years of experience manufacturing and supplying reliable and high-performance Ethernet cables to our clients worldwide. We are the top outdoor Ethernet cable manufacturer. Our cables have a waterproof, UV-resistant jacket for high-speed and reliable connectivity in harsh environments.
We offer the following services for OEMs and startups:
- OEM / ODM Customization
- Research & Development (R&D)
- Prototyping
- High-Volume Manufacturing
- Quality Testing
- Certification
- Private Labeling & Branding
- Custom Packaging & Kitting
- Technical Consultation
- Supply Chain & Logistics
Get In Touch
Our team begins by understanding your technical requirements and application needs. At Wider Cable, our goal is to let our clients focus on their core strengths and help them quickly bring advanced devices to market.
We are a team of highly qualified engineers, material scientists, quality control experts, and logistics coordinators who are always there to help you, no matter what stage of the product development process you are in.
Contact our team of experts today if you are looking for a custom Ethernet cable to fit your device.
