
-
By admin
-
February 19, 2026
- 0 Comment
What is a LAN (Local Area Network)? – Types, Working, & Benefits
The LAN connects digital devices in one physical location, such as a home or office, to enable seamless communication and quick sharing of digital resources. A LAN can be small or large, depending on the number of devices. The most common example is a home Wi-Fi network that connects all family members’ devices to a router and provides internet access.
Before the 1970s, connecting nearby computers or digital devices was just an idea or a concept with limited practical implementations. In 1973, Metcalfe invented Ethernet as a way to link the computers at Xerox’s Palo Alto Research Centre (PARC), which converted a theoretical concept into a functional system. After Metcalfe’s success, Ethernet was standardised and commercialised through industry collaboration, significantly contributing to the global adoption of LAN technologies. Ethernet became the foundation for modern LANs.
This article explains LAN (Local Area Network) in detail. We will dig deep into the benefits, types, and different components that make up a LAN. At the end, we will also understand the quick difference between LAN, MAN, and WAN.
What is a LAN (Local Area Network)?
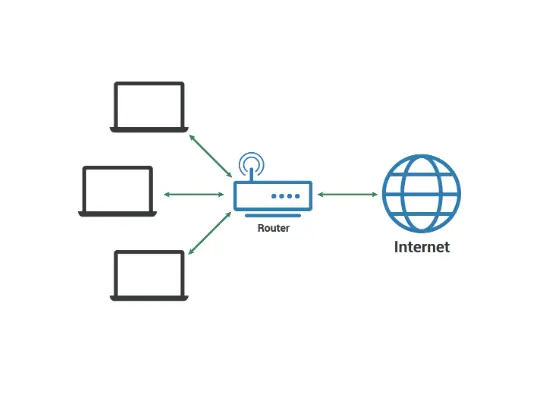
A LAN is a collection of digital devices in one physical location, usually within the same building, like a home or office. Devices in a LAN connect wirelessly (Wi-Fi) or with cables (mostly Ethernet). The main purpose is to enable high-speed communication and file sharing.
The internet is a huge network made up of many smaller networks worldwide. The LAN, or Local Area Network, is one of these. It lets devices connect to the internet or communicate with each other.
For example, if you are at home, the office, or on campus and connected to Wi-Fi, you can browse sites, watch YouTube videos, or send files to the printer. All of this is possible because of a LAN.
How do LANs (Local Area Networks) work?
LAN is one of many types of computer networks. It is mainly used to connect personal computers and workstations in a small area. Typical devices connected to a LAN include:
- Computers
- Smartphones
- Laptops
- Printers
- Routers
In most LANs, the router is the central point that connects other devices to the Internet. It uses both Ethernet and Wi-Fi to connect devices.
- Ethernet: It is a protocol to connect devices physically using Ethernet cables.
- Wi-Fi: We all use WiFi almost daily. It is a protocol to establish a network through radio waves.
Most offices use both wireless (WiFi) and wired (Ethernet) LAN to enable shared access to devices like printers. Anyone connected to the LAN can print files using a single printer. Some organisations set up multiple LANs to provide high-speed and secure communication for each department.
Equipment Needed to Set up a LAN (Local Area Network)
The components of a LAN vary based on the type and purpose of the connection.
For example, most home LANs are set up to provide internet access to all connected devices. A router and a medium (such as Ethernet or WiFi) to connect devices to the router are enough for this type of LAN.
Below are the most common equipment used to set up LANs:
- Router: A central device connecting LANs to the Internet.
- Switch or Access Point: Used to extend the number of devices connected to the LAN.
- Ethernet Cables: A medium that connects different devices to the routers or switches.
- Wireless Access Points: Allow wireless devices to connect to the LAN. These are mainly used for wireless connectivity.
- Modem: Required for internet-connected LANs. It connects your router to the Internet Service Provider (ISP).
Huge LANs, such as the one used in office buildings, utilise multiple routers and switches for exchanging or forwarding the data to the right devices. Such networks require a firewall to prevent intruders from accessing sensitive internal data.
However, it is important to note that not all LANs are implemented to connect devices to the Internet. Most offices or large organisations set up LANs for:
- Local file sharing
- Internal messaging or collaboration
- Resource sharing
- Local application hosting
- Building a centralised storage system
- And more…
Most Common Types of LAN
The network resource organisation and management play a critical role in the overall efficiency of a LAN. Below is the list of the most common technology- and architecture-based LANs.
Architecture-Based LANs
- Client-Server LAN: Clients or devices connect to a central server, which manages file storage, application access, and network traffic. The connection can be wireless or wired, based on the client’s preference. A popular example is Active Directory, managed by Microsoft and mainly used for authentication and authorisation across a network.
- Peer-to-Peer LAN: These smaller networks allow devices to share and request information without a central server. All devices share data and resources through wireless or wired connections to a switch or router. The most common example is a home network using Ethernet or WiFi.
Technology-Based LANs
- Token Ring or ARCNET: These LANs were popular in the 1980s but were replaced by high-performance Ethernet. They use tokens to manage network access, connecting all devices in a circuit. Data is transmitted at up to 100 Mbps around the ring from one device to another.
- Virtual LAN: The virtual LANs are commonly known as the VLANs. Here, the traffic is grouped into separate networks (even when it is physically a part of the same LAN) with the help of technology in the network switch. Such LANs are mostly useful in cases of separating confidential business information for internal purposes. As such, these cloud-based LANs have gained huge popularity over the past decade, mainly due to access control, policy enforcement, network setup, and various security capabilities.
Wired LAN vs. Wireless LAN
The LANs are categorised into two main categories based on how devices are connected to the network: Wired LAN and Wireless LAN. Both have their own advantages and disadvantages. However, wired LANs dominate wireless LANs when it comes to speed and performance. They are ideal for business and campuses that require high-speed, reliable, and secure data connections.
Wired LAN
Wired LANs use cables (mostly Ethernet cables) to connect devices on a network. Nowadays, every computing device has an Ethernet port. LAN cables or Ethernet cables are plugged into this port to enable internet or establish communication between different devices connected to the network.
Such LANs can be found almost everywhere. They are the most common means of connecting computers to gain shared access to servers and devices like printers.
Physical connections of wired LANs are difficult to intercept, so network engineers do not have to worry about eavesdropping and interference. This makes them much more secure than wireless LANs. Many data centres and high-performance computing environments rely on Ethernet-based LANs for daily operations.
Wireless LAN (WiFi)
As the name suggests, this type of LAN connects devices without physical cables. Wireless LANs, or WLANs, transfer data over radio waves. Most WLANs operate on two frequency bands: 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz.
We all know Wi-Fi; it is nothing but a wireless LAN. It is everywhere, from home to office and public places. The main advantage of using a wireless LAN or WiFi is that users can roam around within the constrained space freely and still be able to enjoy the internet and shared resources.
Top 5 Benefits of LAN for Home and Business Networks
A LAN is an integral part of our day-to-day life. For an average user, it is best to connect to the internet or share files between devices within a small physical location. For businesses and large offices, it allows seamless communication and resource (like printers or scanners) sharing.
There are many benefits to establishing a LAN at home or in the office. Below are the top 5 for quick reference.
- Privacy: Local area networks or LANs are private. Businesses can leverage specialised measures to secure networks against unauthorised data access. At Wider Cable, we configure our clients’ LANs with added security features, including firewalls, encryption, authentication, access control, and more.
- Speed: Users can set up their LAN to transmit data at speeds between 100 Mbps and 10 Gbps. They are ideal for data centres and businesses that depend on high-speed data transmission.
- Simplicity: Home LANs are easy to set up. You don’t need to be an expert to enable internet or seamless communication between devices in small areas. Users can access their files from any device on the network.
- Transmission Flexibility: LANs support different transmission mediums such as Ethernet cables, fibre optics, and WiFi. The right choice depends on speed requirements and budget.
- Centralised Control: LAN servers can be set up to centrally store and manage data. This allows administrators to control user accounts and permissions and limit tasks such as software installations.
Drawbacks of Setting Up a LAN for Business Networks
Below are the most common disadvantages of LANs:
- The initial cost of setting up a LAN is high, especially with many devices. Additionally, businesses may need special software to manage their network.
- A LAN can only be implemented and accessed in limited areas of a home, office, campus, or building.
- If the administrator does not maintain LAN integrity and security, unauthorised personnel may access sensitive company data. Continuous administration is essential.
- All administrators can access data stored on devices and the internet history of each and every user accessing the LAN.
- If the server, switch, or access point fails, the entire network is affected. Everything may go down without warning.
FAQs
Q. How do LANs relate to the rest of the Internet?
The internet is a huge network of smaller networks, like a LAN. Each LAN includes a bunch of devices connected together in a small physical location. You may wonder how a LAN is connected to the Internet. It is done through an autonomous system (AS). Your internet service provider (ISP) is an example of AS.
Q. What are the differences between LANs, MANs, and WANs?
A LAN is the most common computer network. The LAN stands for Local Area Network. It includes multiple digital devices. All devices are connected together to ensure communication or file sharing. It is important to note that LAN covers a very small area, like your home or office.
The MAN stands for Metropolitan Area Network. It includes several hundred or thousands of LANs. You may say the MAN covers cities, for instance.
Lastly, the WAN stands for Wide Area Network. It covers the countries. The WAN includes all the LANs available on the internet.
Q. What’s the difference between a LAN and Wi-Fi?
LAN connects devices in a small physical area, like your home or office. Its main purpose is seamless communication between devices. It uses two mediums: WiFi (wireless) and Ethernet (wired).
WiFi is a network technology that enables wireless communication within LANs.
Q. What is a Virtual LAN?
The virtual LANs or VLANs have gained huge popularity in the era of virtualisation and cloud computing. It uses software to divide a physical network into two virtual networks. The goal is to split upcoming traffic and ensure better management.
Q. Are there security risks when using a LAN?
A LAN is a network of devices connected together for quick and efficient file sharing and communication. Such a network uses both wired (Ethernet) and wireless (WiFi) mediums. The wireless communication or WiFi technology is vulnerable to security threats. To prevent security risks, the administrators or network engineers are asked to use firewalls, authentication, encryption, user permissions, and more.
Wider Cable: Leading Manufacturer of Industry-Grade Ethernet Cables
Wider Cable has over 20 years of experience manufacturing and supplying reliable, high-performance Ethernet cables to clients worldwide. We are a top outdoor Ethernet cable manufacturer. We do not just offer off-the-shelf products; our goal is to help clients develop high-performance networking environments.
Our team of experts has helped our clients develop and manage:
- Data Centers
- ISPs and Telecom Networks
- Smart Healthcare Infrastructures
- Highly Reliable Defence Networks
Get In Touch
Our team begins by understanding your technical requirements and application needs. At Wider Cable, our goal is to let clients focus on their core strengths and help them quickly develop advanced systems.
Contact our team of experts today to learn more about our processes and customer testimonials.
